PRODUCTS製品案内
走査型プローブ顕微鏡 Scanning Probe Microscope
attocube社 極低温CFM
attoRAMAN

極低温ラマン顕微鏡

極低温ラマン顕微鏡は、高解像度極低温共焦点レーザ走査型顕微鏡とラマン分光系の組み合わせによりものです。attoRAMANを使うことで最大15Tの磁場中で、極低温下の顕微ラマン分光及び、ラマンイメージを得ることができます。attoRAMANはラマン用レーザー発振器(532nmまたは633nm対応)、冷却裏面照射型CCDの採用、先進のコントローラ/ソフトウェアが付属します。
attoRAMANでは試料の粗動機構としてxyzピエゾステージを使用しており、5mmの可動範囲があります。さらにピエゾスキャナーは、50μmX50μm(室温)、 30μmX30μm(4K)のスキャン範囲があります。ラマンイメージは、試料上をラスタースキャンを行いつつ各点でラマン分光測定を行います。
仕様
| 一般仕様 | |
|---|---|
| 形式 | フリービームによる室温光学系、極低温対応対物レンズ |
| センサーヘッド | 極低温アクロマティック対物レンズ、高NA |
| 共焦点ユニット | |
| 配置 | モジュラーデザインによる多チャンネル光学系 |
| ピンホール | ファイバーアパーチャーをピンホールとして使用(励起光ポート、シグナル光ポート) |
| ピンホールサイズ | ファイバーに依存(3-9µm) |
| 極低温対物レンズ | LT-APO/VIS, LT-APO/VISIR, LT-APO/NIR |
| モニターカメラ | 試料モニター、視野角約54μm(attoDRY使用時), 約40μm(attoLIQUID使用時) |
| 励起 | |
| 励起光波長 | 400-1000nm(標準532nm) |
| 励起光用ポート | FC/APCコネクター(シングルモードファイバ)またはフリービーム導入 |
| 光源 | ラマン用レーザー、シングルモードファイバ結合またはフリービーム結合 |
| レーザーパワー(試料上) | 1 pW- 10 mW |
| フィルター | レーザーラインフィルター |
| 検出 | |
| 検出モード | 2Dラマンイメージ, 時系列及びシングルポイントラマン分光等 |
| 分光器 | 高透過分光器 f=300 mm |
| 光透過率 | >60% (532 nm) |
| フィルター | ダイクロイックミラー及びエッジフィルター(レーザー波長から90 cm |
| グレーティング | 600/mm及び1800/mm |
| 波数分解能 | 1 cm-1 (1800/mmグレーティング使用時) |
| CCDカメラ | 効率90%(532nm), 100kHzリードアウトコンバーター |
| 試料粗動機構 | |
| 移動範囲 | 5 x 5 x 4.8 mm3(オープンループ) |
| ステップサイズ | 0.05..3 µm @ 300 K, 10..500 nm @ 4 K |
| スキャン範囲 | 50 x 50 µm3 @ 300 K 30 x 30 µm3 @ 4 K |
| 試料ホルダー | ASH/QE/0 クイックイクスチェンジ(温度センサー、ヒーター内蔵) |
| 動作環境 | |
| 温度範囲 | 1.5 K..300 K (クライオスタットに依存); mK対応可能 |
| 磁場範囲 | 0..15 T+ (マグネットに依存) |
| 圧力・真空度 | ヘリウム交換ガス中(真空対応可能,10-6 mbar) |
| 設置空間 | |
| ハウジング直径 | 48 mm |
| ボアサイズ | 2インチ (50.8 mm)ボア |
| 対応クライオスタット | attoDRY1000/1100/2100 attoLIQUID1000/2000/3000/5000 |
| エレクトロニクス | |
| スキャンコントローラ | 専用ラマン顕微鏡コントローラ(粗動、スキャンシグナル機能) |
| オプション | |
| クローズドループ粗動機構 | 抵抗式エンコーダー |
| Voigt配置オプション | Voigt,Faraday配置用オプション |
ダウンロード
メーカーサイトへのリンク
アプリケーション
グラフェンのラマン分光
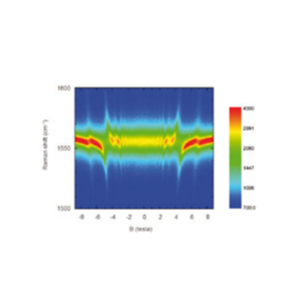
The figure to the left shows magneto-Raman measurements recorded at 4 K on an exfoliated single crystal of natural graphite with unprecedented spatial resolution (approx. 0.5 μm), while sweeping the magnetic field from -9 T to +9 T. The data were recorded on a single graphene flake and demonstrate the crossing of the E2g phonon energy with the electron-hole separation between the valence and conduction Landau levels
(-N,+M) of the Dirac cone. Resonant hybridization of the E2g phonon is a specific signature of graphene flakes which display very rich Raman scattering spectra varying strongly as function of magnetic field [1].
[1] C. Faugeras et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 036807 (2011); (attocube application labs, 2011; work in cooperation with C. Faugeras, P. Kossacki, and M. Potemski, LNCM I – Grenoble, CNRS_UJF_UPS_INSA France)
グラフェンの局所的物性探索のための磁気ラマン分光
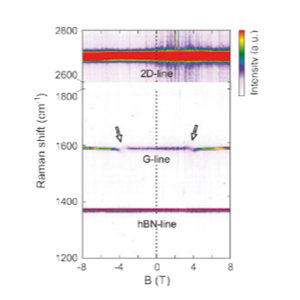
The combination of confocal Raman microscopy and magnetic fields at 4 K yields the opportunity to investigate and tune the electron-phonon interaction in graphene and few-layer graphene. In particular, excitations between Landau levels can resonantly couple to the Raman active long wavelength optical phonon (G-phonon), when their energies are matched, resulting in magneto- phonon resonances (MPRs). Such resonances at ±3.7 T are presented in the figure and highlighted by arrows. The details of the coupling depend on various material properties of the investigated graphene layer. From the MPRs, device parameters such as the electron-phonon coupling constant or the Fermi velocity of the charge carriers can be extracted. Interestingly for low charge carrier doping, the Fermi velocity shows signatures of many-bod interaction effects [2].
[2] Nat Comms, Nature Publishing Group, 2015, 6, 8429
